1 in 5 Adults Grapple with Severe Gum Disease Globally
According to the ADA article “Stepping up in 2023: Periodontics is breaking new ground,” the FDI World Dental Federation reports that roughly a fifth of the world’s adult population is affected by severe periodontal disease, which amounts to more than 1 billion cases globally. It’s essential to understand periodontal disease to maintain a healthy smile. Let’s delve into the details of what periodontal disease entails. We will explore its risk factors and highlight the importance of seeking proper diagnosis and treatment. Join us on this informative exploration.
What is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, unfolds in two main stages. The first stage is gingivitis. If not treated, it advances to periodontitis, the second stage. These stages highlight the progression of periodontal disease, impacting oral health differently.
What is Gingivitis?
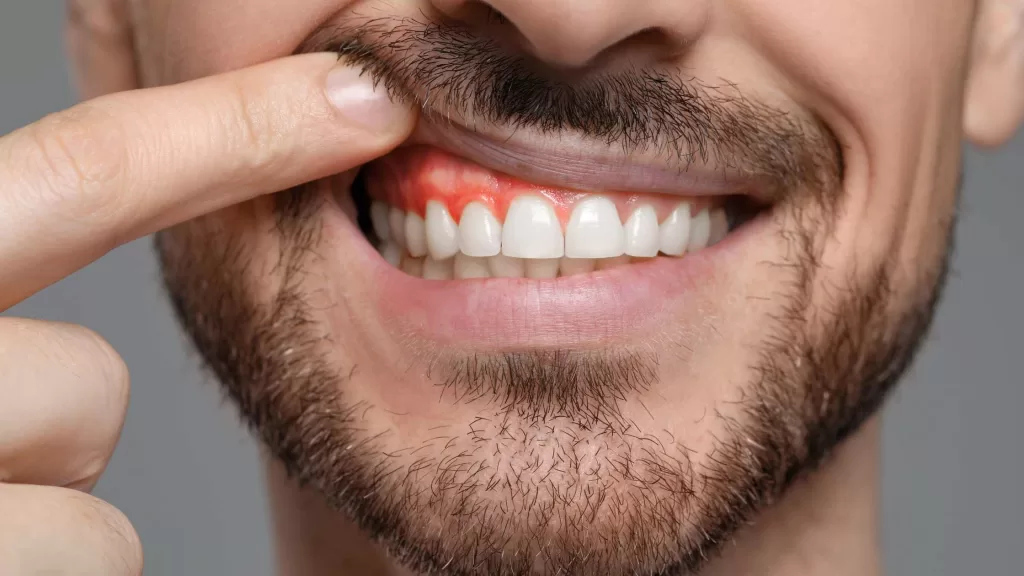
Gingivitis is the start of a more serious gum problem. First, you might notice your gums bleed when you brush or floss. This bleeding happens because of swelling, which is your body’s way of fighting off plaque or tartar on your teeth. Luckily, if you catch it early, you can fix the damage. Just be sure to keep your teeth clean and visit the dentist for some extra help. As at this stage, the damage is usually reversible with proper oral hygiene and professional care.
Plaque buildup often comes from not brushing well or skipping flossing. But it’s not always about brushing or flossing. Sometimes, medications change your mouth’s environment. Dehydration or mouth breathing can also play a role. In fact, many factors can contribute to plaque buildup.
What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis is the secondary stage of the disease if chronic gingivitis goes untreated. Unlike gingivitis, periodontitis involves irreversible damage to the gums and underlying bone supporting the teeth. It’s essentially like a house with termites or rotting beams – the tissues that support the teeth are eroding and cannot be regenerated. Plaque then transforms into tartar or calculus, a hard deposit on the tooth root under the gums.
This substance is so tough that only a professional cleaning can remove it. As a result, “pockets” of space form between the gums and teeth. These pockets become a breeding ground for bacteria and trapped food. Consequently, they cause further inflammation. This ongoing inflammation eventually results in bone loss and, ultimately, tooth loss.
Understanding the Difference: Gingivitis vs. Periodontitis

The source of the picture is “New fact sheet – Periodontal (gum) disease” from the ADA Victoria branch website. For additional details, please refer to the hyperlink above.
Gingivitis:
The initial stage of gum disease characterised by inflamed, bleeding gums. With proper care, gingivitis is reversible and does not involve permanent damage to the supporting structures of the teeth.
Periodontitis:
An advanced stage of gum disease where the inflammation and damage extend beyond the gums to affect the bone supporting the teeth. Without treatment, periodontitis can lead to irreversible damage and tooth loss, as well as shrinking of the head and face structures causing loose/wrinkled lips.
Risk Factors for Periodontal Disease
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, to accumulate and cause gum disease.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: Tobacco use weakens the immune system and makes it harder for the gums to heal. (new evidence indicates vaping is also included)
- Genetics: Some individuals are more predisposed to periodontal disease due to their genetic makeup.
- Systemic Diseases (Commonly auto-immune diseases): Conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases can increase the risk and severity of gum disease.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can make gums more susceptible to gum disease.
- Medications: Certain medications can affect oral health by reducing saliva flow or causing gum overgrowth.
- Poor Nutrition: A diet lacking in essential nutrients can compromise the body’s ability to fight off infections, including gum disease.
Seeking Proper Diagnosis and Treatment
Periodontal disease can be insidious, often progressing painlessly until it reaches an advanced stage. This is why regular dental check-ups are crucial. At Grange Family Dental, our team uses advanced diagnostic tools like X-rays and periodontal disease charting to thoroughly screen and diagnose gum disease.
We follow the Periodontal Disease Staging and Grading Table from the latest Periodontal and Peri-Implant Disease Diagnosis and Classification Proposal of 2017. This comprehensive tool, developed through international collaboration, ensures accurate staging and grading for effective treatment planning.
If you are concerned you may have gingivitis or periodontitis, act now!
Your oral health matters. Don’t let periodontal disease sneak up on you. Therefore, act now and book your check-up at Grange Family Dental. Our experts will then conduct a thorough examination, including X-rays and periodontal charting. This approach ensures you receive the best care, utilising the latest techniques in periodontal diagnosis and treatment.
Also, remember, early detection and intervention are key to preventing the progression of gum disease and preserving your beautiful smile. Don’t wait for symptoms to appear. Book your appointment today at Grange Family Dental and take the first step toward optimal oral health.
*Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Please consult with your dentist or healthcare provider for personalised diagnosis and treatment.
Read more about Periodontal diseases
New fact sheet – Periodontal (gum) disease
Exploring Natural Remedies for Fighting Gum Disease
Top Signs and Symptoms of Gum Disease: What You Need to Know